White Beans in Different Culinary Applications
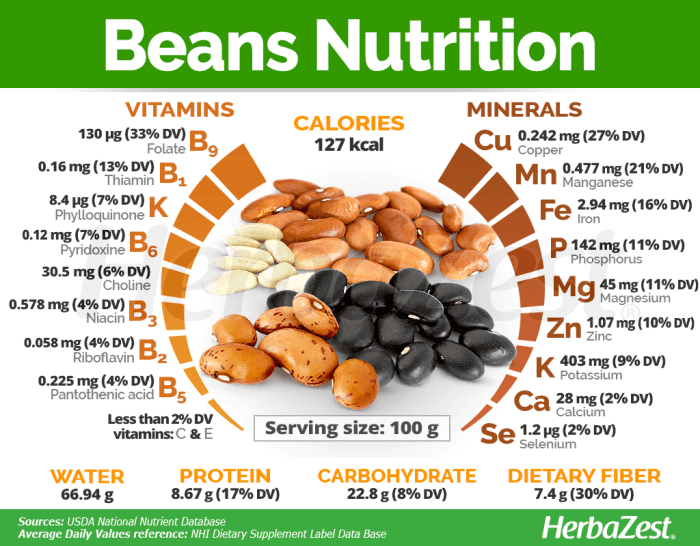
White beans nutrition facts – Yo, Medan peeps! Let’s dive into the amazing versatility of white beans – they’re not just for grandma’s soup anymore! These little guys are a culinary chameleon, showing up in dishes all over the world, from simple to super sophisticated. Get ready to be amazed!
White beans, a staple in Maluku cuisine, offer a hearty dose of fiber and protein. For those seeking a contrasting nutritional profile, consider comparing their values to the sausage patty nutrition facts , which often highlight higher fat content. Returning to the humble white bean, remember its versatility in various dishes, enriching our meals with essential nutrients and a satisfying taste.
Global Uses of White Beans
White beans are a global superstar, finding their way into countless dishes across various cultures. Their mild flavor and creamy texture make them incredibly adaptable. Here’s a quick peek at their worldwide adventures:
- Italy: Think creamy cannellini beans in pasta e fagioli (pasta and bean soup), or forming the base of a rich, flavorful minestrone.
- Mexico: Refried beans (frijoles refritos) are a staple, often served with tortillas and all sorts of yummy toppings. They’re also a key ingredient in many stews and chilies.
- France: Cassoulet, a hearty stew featuring white beans, sausage, and duck confit, is a true French classic. Think rustic, comforting, and seriously delicious.
- India: Rajma masala, a flavorful curry made with kidney beans (a type of white bean), is a popular vegetarian dish. The spices and creamy beans are a match made in heaven.
- Middle East: White beans are often used in salads, stews, and dips, adding a hearty texture and subtle flavor.
White Bean Recipe Examples
Creamy White Bean and Spinach Pasta
Ingredients: 1 tbsp olive oil, 1 onion (chopped), 2 cloves garlic (minced), 1 (15-ounce) can cannellini beans (rinsed and drained), 5 oz fresh spinach, 1 cup vegetable broth, salt and pepper to taste, 1/2 cup grated Parmesan cheese, pasta of your choice. Instructions: Sauté onion and garlic in olive oil until softened. Add beans, spinach, and broth. Simmer until spinach is wilted.
Season with salt and pepper. Toss with cooked pasta and Parmesan cheese. Serve hot and enjoy the simple goodness!
Roasted White Bean and Vegetable Salad
Ingredients: 1 (15-ounce) can cannellini beans (rinsed and drained), 1 red bell pepper (chopped), 1 zucchini (chopped), 1 red onion (chopped), 2 tbsp olive oil, 1 tbsp balsamic vinegar, 1 tsp dried oregano, salt and pepper to taste. Instructions: Preheat oven to 400°F (200°C). Toss vegetables and beans with olive oil, balsamic vinegar, oregano, salt, and pepper. Spread on a baking sheet and roast for 20-25 minutes, or until vegetables are tender and slightly browned.
Serve warm or at room temperature. This is perfect for a light yet satisfying lunch!
White Bean and Chorizo Stew
Ingredients: 1 tbsp olive oil, 1 lb chorizo sausage (sliced), 1 onion (chopped), 2 cloves garlic (minced), 1 (15-ounce) can cannellini beans (rinsed and drained), 1 (14.5-ounce) can diced tomatoes, 4 cups vegetable broth, 1 tsp smoked paprika, 1/2 tsp cumin, salt and pepper to taste. Instructions: Brown chorizo in olive oil. Add onion and garlic, sauté until softened.
Stir in beans, tomatoes, broth, paprika, and cumin. Season with salt and pepper. Bring to a boil, then reduce heat and simmer for 20 minutes. This rich and flavorful stew is perfect for a chilly evening.
Nutritional Comparison of White Bean Preparations, White beans nutrition facts
The nutritional content of white beans can vary slightly depending on how they’re prepared. Generally, dried beans are slightly higher in fiber and protein compared to canned beans because of the processing involved. However, canned beans offer convenience. Boiling beans helps retain nutrients, while roasting can slightly reduce some water-soluble vitamins but adds a nice smoky flavor. The differences aren’t drastic, but it’s something to keep in mind when planning your meals.
Think of it like this: dried beans are the champions of fiber, while canned beans are the kings of convenience. Roasted beans? They’re the flavor MVP!
Potential Drawbacks and Considerations

Okay, so we’ve talked about how awesome white beans are, but like, every food has a flip side, right? Let’s get real about some potential downsides and things to keep in mind when you’re chowing down on these little nutritional powerhouses. It’s all about balance, la!
White beans, while generally safe and beneficial, contain certain compounds that can affect some people. Understanding these potential drawbacks and how to manage them is key to enjoying the benefits of white beans without any unwanted side effects. We’re talking about maximizing the good vibes and minimizing the, well, not-so-good vibes.
Antinutrients in White Beans and Mitigation Strategies
White beans, like many legumes, contain antinutrients. These aren’t necessarily “bad,” but they can interfere with the absorption of certain nutrients. Phytates, for example, bind to minerals like iron and zinc, reducing their bioavailability. Lectins are another type of antinutrient that can cause digestive upset in some individuals. The good news?
Simple cooking methods can significantly reduce the impact of these antinutrients. Soaking the beans overnight before cooking breaks down some of these compounds, and proper cooking (boiling for at least 10 minutes) further reduces their levels. Sprouting beans is another effective method to reduce antinutrient levels, making them easier to digest and increasing nutrient availability. Think of it as prepping your beans for maximum absorption.
Potential Interactions with Medications
Certain medications can interact with the compounds in white beans. For example, white beans are high in fiber, which can sometimes affect the absorption of certain medications. If you’re on medication, especially those that need to be absorbed in the intestines, it’s always a good idea to chat with your doctor or pharmacist. They can advise you on any potential interactions and whether adjusting your medication timing or dosage is necessary.
Don’t just assume everything’s cool; a quick check with a healthcare professional is always a smart move.
Recommended Serving Sizes of White Beans
Portion control is key, even with something as healthy as white beans. A general guideline for adults is around ½ to 1 cup of cooked white beans per serving. For children, portion sizes should be adjusted according to their age and overall dietary needs. Remember, it’s not about restricting yourself; it’s about enjoying white beans as part of a balanced diet.
Too much of anything can lead to digestive issues, so listen to your body.
Proper Storage of White Beans to Maintain Nutritional Value
Storing your beans correctly is crucial for maintaining their freshness and nutritional value. Dried white beans should be stored in an airtight container in a cool, dark, and dry place. They can last for a year or more if stored properly. Cooked white beans should be refrigerated and consumed within 3-4 days to prevent spoilage. Freezing cooked white beans is also a great option to extend their shelf life, keeping them fresh and ready for your next culinary adventure.
Proper storage is like giving your beans a VIP treatment, ensuring they stay at their peak performance.
Question Bank: White Beans Nutrition Facts
Are white beans good for weight loss?
Yes, their high fiber and protein content promote satiety, helping manage appetite and potentially aiding weight management.
Can I eat white beans every day?
Moderation is key. While beneficial, daily consumption might lead to digestive discomfort for some due to the high fiber content. Listen to your body.
Do white beans cause gas?
Yes, like other legumes, white beans contain raffinose, a sugar that can cause gas for some people. Soaking and proper cooking methods can help reduce this effect.
How long can I store dried white beans?
Dried white beans, stored in an airtight container in a cool, dark, and dry place, can last for up to a year.



