Health Benefits and Risks Associated with Coconut Milk Consumption: Coconut Milk Nutrition Facts

Coconut milk nutrition facts – Coconut milk, a popular ingredient in many cuisines worldwide, presents a complex nutritional profile, sparking ongoing debate about its overall health impact. While touted for its purported benefits, a critical examination reveals both advantages and significant drawbacks, particularly concerning its saturated fat content and potential implications for cardiovascular health. Understanding these nuances is crucial for making informed dietary choices.
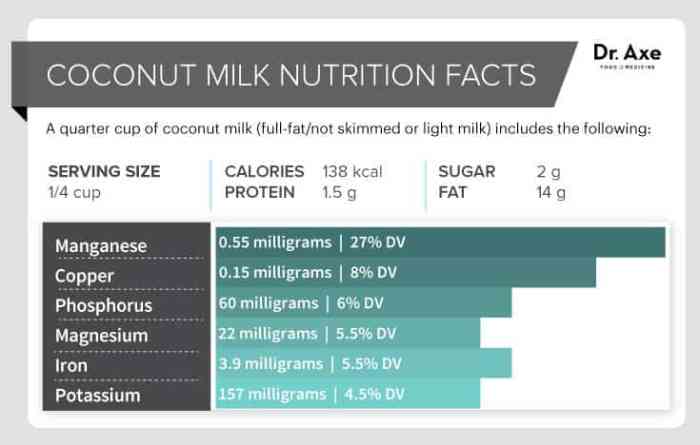
Dietary Fiber and Micronutrients in Coconut Milk
Coconut milk, particularly the full-fat variety, contributes to dietary fiber intake. Fiber plays a crucial role in digestive health, promoting regularity and potentially reducing the risk of certain gastrointestinal issues. Furthermore, coconut milk contains small amounts of various micronutrients, including manganese, which is essential for bone health and metabolism. However, it’s crucial to note that these contributions are relatively modest compared to other dietary sources rich in fiber and these specific minerals.
Relying solely on coconut milk for these nutrients would be a nutritional oversight.
High Saturated Fat Content and Cardiovascular Health Risks
The significant drawback of coconut milk is its high saturated fat content. Saturated fats have been linked to increased levels of LDL cholesterol (“bad” cholesterol), a major risk factor for heart disease. While some argue that the medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) in coconut milk may offer metabolic advantages, the overwhelming evidence points towards a potential negative impact on cardiovascular health, especially with excessive consumption.
Numerous studies have demonstrated a correlation between high saturated fat intake and an increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular complications. This risk is amplified by individuals already predisposed to such conditions.
Coconut Milk’s Role in a Balanced Diet, Coconut milk nutrition facts
Incorporating coconut milk into a balanced diet requires careful consideration. It should not be viewed as a health food in itself, but rather as a flavorful ingredient to be used sparingly. Over-reliance on coconut milk as a primary source of fat and nutrients can lead to an unbalanced intake, potentially compromising overall health. A balanced diet emphasizes a variety of nutrient-rich foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, while minimizing the consumption of highly saturated fat sources like coconut milk.
Yo, so you’re checking out coconut milk’s nutritional breakdown, right? It’s pretty legit for healthy fats, but if you’re looking for a different protein punch, check out the nutritional info for low fat greek yogurt 200g nutrition facts – it’s a solid comparison. Then get back to those coconut milk facts – gotta know your options, lah!
Moderation is key.
Overall Health Impact of Moderate Coconut Milk Intake
Moderate consumption of coconut milk, as part of a balanced and varied diet, is unlikely to pose significant health risks for most individuals. However, excessive intake can contribute to weight gain and increase the risk of cardiovascular problems. The benefits, such as the modest contribution to fiber and certain micronutrients, are outweighed by the potential negative consequences associated with its high saturated fat content if consumed in large quantities.
Therefore, incorporating coconut milk into one’s diet should be approached with caution and mindful moderation.
Coconut Milk in Different Forms
The market for coconut milk, a product once relegated to niche ethnic grocery stores, has exploded. This expansion, however, has brought with it a bewildering array of options, leaving consumers grappling with the nutritional implications of choosing between full-fat, light, low-fat, canned, and homemade varieties. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed choices that align with individual dietary goals and health concerns.
The following analysis dissects the nutritional landscape of coconut milk’s diverse forms, exposing the often-hidden realities of processing and marketing.The nutritional profile of coconut milk varies dramatically depending on its fat content and processing method. While full-fat coconut milk offers a rich source of healthy fats, light and low-fat versions undergo significant alterations that impact their nutritional value and overall health benefits.
These changes are rarely presented transparently, necessitating a critical examination of the industry’s marketing practices.
Nutritional Differences Between Full-Fat, Light, and Low-Fat Coconut Milk
The primary difference between these varieties lies in their fat content. This, in turn, significantly affects their caloric density and the proportions of other macronutrients. Reducing fat content often involves removing the cream, a process that impacts the overall nutritional profile.
- Full-Fat Coconut Milk: High in saturated fat (primarily medium-chain triglycerides or MCTs), moderate in carbohydrates, and low in protein. The high fat content contributes significantly to its caloric density.
- Light Coconut Milk: Contains significantly less fat than full-fat, resulting in a lower calorie count. The reduction in fat also leads to a decrease in MCTs. Carbohydrate content may be slightly higher due to the removal of fat.
- Low-Fat Coconut Milk: The lowest in fat, with a corresponding reduction in calories. The nutritional profile is further altered through processing, potentially leading to changes in texture and taste.
Note: Precise nutritional values vary depending on the brand and specific product. Always check the nutrition label for accurate information. The industry’s lack of standardization makes direct comparisons challenging, highlighting the need for greater transparency.
Impact of Processing Methods on Coconut Milk Nutrition
Processing significantly alters the nutritional composition of coconut milk. Heat treatment, homogenization, and the addition of stabilizers and emulsifiers all affect the final product. These processes, while improving shelf life and consistency, often come at the expense of some nutritional components, particularly heat-sensitive vitamins and antioxidants. For example, high-temperature processing can reduce the levels of certain beneficial compounds.
The use of additives, while often deemed safe, raises concerns about potential long-term health effects, an area requiring further rigorous investigation.
Nutritional Comparison: Canned vs. Fresh Coconut Milk
Canned coconut milk, ubiquitous in supermarkets, undergoes extensive processing, including heat treatment and packaging. This processing, while ensuring extended shelf life, may lead to nutrient degradation compared to milk extracted from fresh coconuts. Fresh coconut milk, made from the flesh of a freshly cracked coconut, boasts a higher concentration of bioactive compounds and naturally occurring nutrients, though its shorter shelf life presents a challenge for widespread consumption.
The convenience of canned milk often overshadows the potential nutritional advantages of the fresh alternative.
Making Coconut Milk from Scratch: Nutritional Value
Making coconut milk at home offers a degree of control over the ingredients and processing methods. This allows for a potentially more nutrient-rich product compared to many commercially available options. The process involves grating fresh coconut flesh, blending it with water, and straining the mixture. The nutritional value of homemade coconut milk closely mirrors that of fresh coconut milk, provided minimal processing and heat are used.
However, the effort and time involved are significant deterrents for many consumers, highlighting the ongoing tension between convenience and nutritional quality in the modern food system.
Essential Questionnaire
Is coconut milk good for weight loss?
While coconut milk can be part of a weight-loss diet, its high calorie and fat content means it should be consumed in moderation. Focus on portion control.
Can I use coconut milk in baking?
Absolutely! Coconut milk adds richness and moisture to baked goods. Just be mindful of its fat content when adjusting other ingredients.
Is coconut milk suitable for people with allergies?
Coconut milk is a common allergen, so individuals with coconut allergies should avoid it. Always check labels carefully.
Does coconut milk expire?
Yes, canned coconut milk has a shelf life. Check the “best by” date on the can and refrigerate after opening.



